Abstract
Background: Systemic mastocytosis (SM) is a disorder of neoplastic mast cells ranging from indolent to aggressive multi-system disease. We previously reported our large single centre experience managing SM. Since 2019 patients have had access to new treatments within trials. Prognostic scoring systems developed in SM to improve outcome predictions and guide treatment have been a focus of recent studies, although are yet to be validated in real-world setting. We sought to apply these scoring systems within our UK cohort, with a particular focus on the international prognostic score (IPSM) and the mutation-adjusted risk score (MARS).
Methods: We performed a retrospective study of 192 adult patients diagnosed with SM between 2009 and 2021 including demographics, clinical data, as well as next generation sequencing (NGS) based myeloid gene panels carried out in advanced SM patients (AdvSM) where available. Prognosis for all patients was calculated based on IPSM (Sperr et al. [2019]) in all our SM patients and MARS scores in those with AdvSM (Jawhar et al. [2019]).
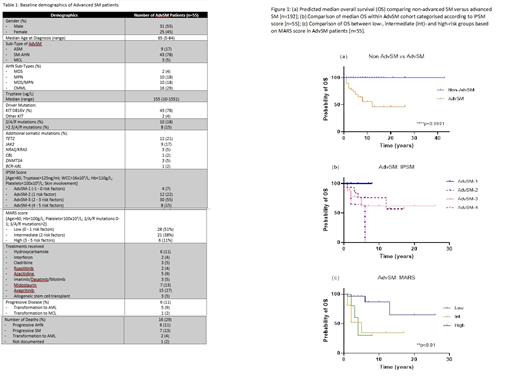
Results: There was no gender bias in our cohort with 87 (46%) males and 105 (54%) females. Median age at diagnosis was 52 years (range 5-84) and majority of patients had indolent SM (ISM; 129/192 [67%]), 8/192 (4%) smouldering SM (SSM) and 55/192 (29%) advanced SM (AdvSM). In those with AdvSM, 43/55 (78%) had an associated haematological neoplasm (SM-AHN); 9/55 (17%) aggressive SM (ASM) and 3/55 (5%) mast cell leukaemia. As expected, AHN sub-types were myeloid with majority being CMML (16/55; 29%) [Table 1]. Median tryptase at diagnosis in ISM patients was 41ug/L (range 3-351ug/L), while in SSM it was 494ug/L (range 174-682ug/L) and in AdvSM it was 155ug/L (range 10-1551). Most patients were positive for the KIT D816V mutation (131/192; 68%).
As expected, ISM and SSM (non-AdvSM) patients had better prognosis compared to those with AdvSM [Figure 1a], with median overall survival (OS) not reached in the former and 12 months in the latter with 11-year follow-up.
We next applied the IPSM score to the AdvSM cohort, with the largest proportion categorised as AdvSM-3 (25/55; 45%) while 10/55 (18%) were AdvSM-4 [Table 1]. Survival outcome was notably higher in the AdvSM-1 group (4/55; 7%) with no deaths recorded, while 6/25 (24%) and 4/10 (40%) deaths were reported in AdvSM-3 and AdvSM-4 groups respectively [Figure 1b].
SM patients are known to carry somatic mutations in addition to KIT, in particular SRSF2, ASXL1 and RUNX1 (S/A/R) which are associated with adverse outcome. In our AdvSM cohort, 10/55 (18%) of patients were positive for one of these mutations on NGS-based myeloid gene panel and 8/55 (15%) carried ≥2. Additional clinically significant mutations are summarised in Table 1.
We next examined the MARS score; most of our AdvSM patients categorised as low-risk (28/55, 51%), 21/55 (38%) were intermediate-risk and 6/55 (13%) high-risk [Table 1]. Survival outcome as expected in the low-risk group was higher compared to the intermediate- and high-risk groups, with 10-year OS of 87% versus 35% and 30% respectively [Figure 1c].
On reviewing our AdvSM cohort, 6/55 (11%) had progressive disease: 5 transforming to acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) and 1 to mast cell leukaemia (MCL). Interestingly, when reviewing cause of death, the highest proportion were due to AHN progression (6/16; 38%) while 2/16 (13%) were from transformation to AML [Table 1].
As expected within our cohort, there was a discrepancy between the IPSM and MARS scores as the latter includes the presence of S/A/R mutations. 2 patients diagnosed with MCL in 2016 and 2019 respectively, were categorised high risk based on both scores. Both are alive to date having received the KIT inhibitor avapritinib, with one continuing on this treatment. The other progressed to AML and underwent allogeneic stem cell transplant, with ongoing complete remission. Other treatments received by our AdvSM patients are summarised in Table 1.
Conclusion: Application of the IPSM and MARS prognostic scores to our data reflects findings of other groups with better outcomes seen in non-AdvSM compared to AdvSM patients. Furthermore, although our AdvSM cohort is small, the presence of adverse risk factors could be overcome through recent advances in treatments and consolidation with stem cell transplant. Hence, identification of high-risk patients using these prognostic scores can direct targeted first-line therapy and improve outcomes.
Sriskandarajah: Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Other: Education. Green: Novartis: Other: Education. Ong: Novartis: Other: Education. Harrison: Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; CTI BioPharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Gilead Sciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Incyte Corporation: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Constellation Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Geron: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Keros: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Galacteo: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Sierra Oncology: Honoraria; AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Promedior: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Grattan: Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Radia: Blueprint Medicines Corporation: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Study steering group member, Research Funding; Cogent Biosciences Incorporated: Other: Study Steering Committee; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Education events; EXPLORER and PATHFINDER studies: Other: Member of the Response Adjudication Committee.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract